Read on to learn more about:
- What is Caprylic Acid Exactly?
- The Researched Benefits of Caprylic Acid
- Caprylic Acid C8 MCT vs. Generic MCT Products
- C8 MCT vs. C10 MCT
- How to Use C8 MCT Optimally
- Comparison of C8 MCT Products / Which are Worth Your Money?
Caprylic Acid Overview
Fatty acids come in two forms: saturated and unsaturated.
Caprylic acid is a saturated fatty acid. Chemical classification of saturated fatty acids looks at how many carbon atoms are found in the hydrocarbon chain:
- Less than 6 carbons denotes short-chain fatty acids (SCTs)
- 6-12 carbons denotes medium-chain fatty acids (MCTs);
- more than 12 carbons denotes long-chain fatty acids (LCTs);
- and more than 22 carbons denotes very long-chain fatty acids.
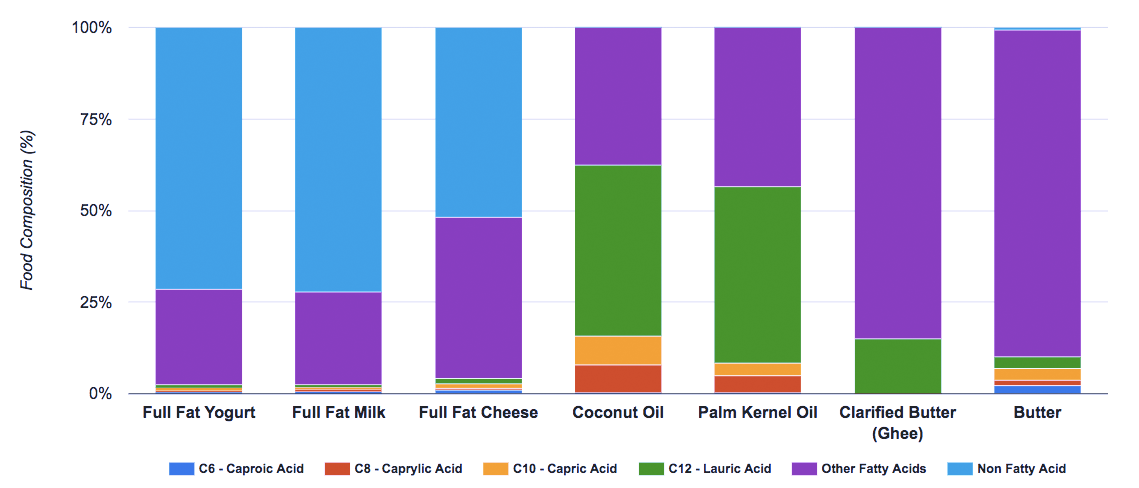
Caprylic acid (C8) has 8 carbons and it falls into the MCT category. For this reason it is often called C8 MCT. You find C8 MCT in food products like coconut, palm and butter.
C8 MCT has fewer carbons (8 carbons) compared to capric acid (C10) and lauric acid (C12). This is the reason why it has a better ketone producing profile compared to the longer carbon MCT’s.
C8 MCT products come from palm and coconut oils. Removing the other fatty acids leaves the pure C8 MCT. The result is an oil composed of only caprylic acid.
Typical Fatty Acid Composition of Foods Containing MCTs
What About C6?
C6, Caproic acid is the lowest carbon MCT. It is more effective at raising ketone levels than C8. This is due to its lower carbon number. Research shows that it induces higher ketone levels in animals than the other MCT oils.
Right now, C6 MCT oil is not available. C6 is generally excluded from MCT oil because it is such a small component in palm and coconut oil products. Unlike C8, high quantities are not found in coconut and palm oils. Instead, C6 is present in various animal fats.[note]Schultz, L.H., Smith, V.R., Lardy, H.A (1949). The effect of the administration of various fatty acids on the blood ketone levels of ruminants. Journal of Diary Science, 32, 817 – 822.[/note]
What is & What Isn’t Caprylic Acid? Clearing Up Naming Confusion
Several different names are commonly used to refer to Caprylic Acid (C8). This creates a lot of confusion, as they are not the same.
Caprylic acid’s hydrocarbon chain contains 8 carbon atoms. It can be referred to as C8 or octanoic acid. Octo, of course, referring to the number 8.
The name caprylic triglyceride or caprylic acid triglycerides are also sometimes used. These are different molecules compared to caprylic acid, which is a free fatty acid. With these triglycerides, a glycerol molecule is bound to three caprylic fatty acids.
Triglycerides break down into the C8 found in MCT oil so it is common to see the term ‘caprylic triglyceride’.
Functionally, caprylic acid and caprylic acid triglyceride are the same. The pancreas secretes an enzyme called lipase that breaks down these triglycerides. This produces three fatty acids and a glycerol molecule. Once the lipase breaks down the triglyceride oil it becomes simple Caprylic Acid. The last step is the conversion into ketones in the same way as the stand alone Caprylic Acid.
Caprylic Acid Benefits & Supporting Literature
Research has shown that caprylic acid (C8) ingestion increases ketone production.[note]McGarry, J. D., & Foster, D. W. (1971). The Regulation of Ketogenesis from Octanoic Acid The Role of the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and Fatty Acid Synthesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 246(4), 1149-1159.[/note],[note]Miles, J. M., Haymond, M. W., Nissen, S. L., & Gerich, J. E. (1983). Effects of free fatty acid availability, and insulin deficiency on ketone production in postabsorptive man. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 71(6), 1554.[/note]
Just a small increase of 1mMol in plasma caprylic acid levels will increase ketone production five fold. This is what keto dieters want since ketones are their primary source of energy.
Moreover, despite the presence of moderate amounts of blood glucose (such as when you’ve been eating carbs or higher amounts of protein), caprylic acid is still readily absorbed from the gut.[note]Schwabe, A. D., Bennett, L. R., & Bowman, L. P. (1964). Octanoic acid absorption and oxidation in humans. Journal of applied physiology, 19(2), 335-337.[/note]
Therefore, the C8 converts into ketones regardless of whether you are in ketosis and following a keto diet or not. However, scientific research is still at an early stage. It is not clear yet what long-term effect elevated ketone levels when combined with a high carb diet has on the body.
Alongside this, other research shows that caprylic acid has strong antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activities[note]Nair, M. K. M., Joy, J., Vasudevan, P., Hinckley, L., Hoagland, T. A., & Venkitanarayanan, K. S. (2005). Antibacterial effect of caprylic acid and monocaprylin on major bacterial mastitis pathogens. Journal of dairy science, 88(10), 3488-3495.[/note] and improves blood lipid profiles of hypertensive rats. Unfortunately, data in humans is limited.[note]Kim, B. H., Sandock, K. D., Robertson, T. P., Lewis, S. J., & Akoh, C. C. (2008). Dietary structured lipids and phytosteryl esters: blood lipids and cardiovascular status in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Lipids, 43(1), 55-64.[/note]
However, there is little evidence supporting the idea that caprylic acid is better than a mixture of MCT’s in reducing body-fat. Research on the performance-enhancing benefits of caprylic acid is also limited.
Caprylic Acid (C8) Products
Caprylic Acid (C8) vs. MCT Oil Products
Something to consider is that most MCT oils products are generally a mixture of caprylic acid and capric / decanoic acid (C10) and sometimes lauric acid (C12). The exact ratio of each varies by product and contains between 50 to 75% caprylic acid.
MCT oil has built a healthy amount of research in peer-reviewed studies over the past few decades. Many of its benefits come from caprylic acid. This is because caprylic acid makes up the majority /50% of the mixture. That said, MCT products are not identical to pure caprylic acid products. Be careful not to confuse the two.
Typical Fatty Acid Composition of Oil Products (MCT, Coconut, Palm, C8)
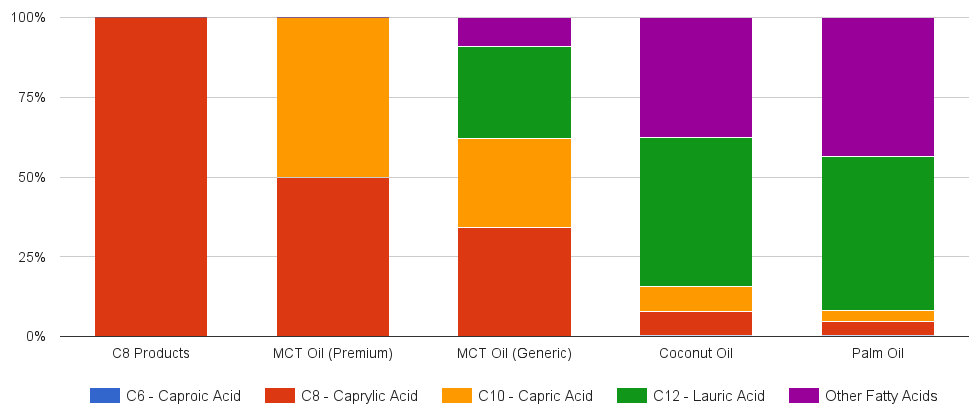
C8 products are a refined version of MCT oils that have had the capric acid (C10) and lauric acid (C12) removed. This leaves only caprylic acid as the fatty acid component.
This improves gut tolerability, a common issue with MCT oil. GI distress, indigestion, and diarrhoea can result in those new to MCT oils or if doses are over a tablespoon. Caprylic acid has a shorter hydrocarbon chain than capric and lauric acids. Therefore it seems to pass through the GI tract quicker. It is quickly moved out to the liver for metabolism. This may help to reduce the GI distress felt with MCT oils.
Caprylic Acid (C8) vs. Capric Acid (C10) Ketone Production
Recent research from Cunnane et al. [note]
Vandenberghe, C., St-Pierre, V., Pierotti, T., Fortier, M., Castellano, C. and Cunnane, S. C.
Vandenberghe, Camille et al. “Tricaprylin Alone Increases Plasma Ketone Response More Than Coconut Oil Or Other Medium-Chain Triglycerides: An Acute Crossover Study In Healthy Adults.” Current Developments in Nutrition 1.4 (2017): e000257. Web. 11 Aug. 2019.
[/note] shows how much more effective caprylic (C8) acid is versus capric acid (C10) in its ability to raise ketones.
The following graph is a clear representation of the difference between caprylic acid (C8), capric acid (C10), coconut oil (CO) and MCT oil (C8/C10) on the total ketone levels over an 8-hour period. C8 increases ketones by approximately 3 times more than C10.
Plasma Ketone Increases from C8, C10 and Coconut Oil Compared
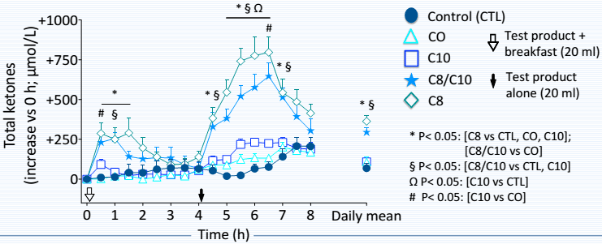
This research suggests that caprylic acid is the main contributor to elevated ketone levels in MCT oil (C8/C10). C10 shows little improvement compared to coconut oil and the control sample.
The low ketone levels in the coconut oil sample also support this. The very low caprylic acid levels present in coconut oil have little impact on ketone levels compared to the control sample. This confirms anecdotal evidence that coconut oil fails to give the feeling of ‘ketosis’ like MCT oil or caprylic acid.
It is also worth noting that all samples taken without food had a marked improvement in ketones when compared to the samples taken with breakfast (i.e. with a meal).
How and When to Use Caprylic Acid
To maximize the benefits of using Caprylic Acid follow these guidelines:
- Since caprylic acid is readily digested by the liver and used for energy, it is ideal to take it before training (roughly 30-45 minutes pre-workout) without a meal (especially for those on keto diets). If taken with a meal, take at least an hour before training. The same advice goes for other energy boosting goals, e.g. mental focus.
- C8 can augment meals that are higher in carbs and/or protein to reduce blood glucose spikes. This happens because insulin levels rise after ingestion of caprylic acid, due to increases in ketone production. This increases glucose clearance. Although this can vary widely from person to person.
- Take it at any other time of the day to fulfil your fat intake needs. However, C8 is a “pricey” source of dietary fat.
- For antimicrobial use follow the directions on the product label and apply to the treatment area.
Caprylic Acid Dosage: How Much Should You Use?
In general, one to two tablespoons (15 – 30mL) of pure caprylic acid oil at a time is sufficient.[note]Scalfi, L., Coltorti, A., & Contaldo, F. (1991). Postprandial thermogenesis in lean and obese subjects after meals supplemented with medium-chain and long-chain triglycerides. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 53(5), 1130-1133.[/note] Some people will go up to three tablespoons at a time, but the added benefits of such a high dose at one time are questionable. It would be ideal to spread several small doses over the day as opposed to “loading” at one time.
Caprylic Acid (C8) Products Available Now
| Company | Product Name | Size (Oz) | Size (ml) | 15ml Doses Included | Price (£ GBP) | Price per Dose (£ GBP) | Purity | Other Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulletproof | Brain Octane | 16 | 473 | 32 | 16.95 | 0.53 | N/A* | Sourced from Coconut Oil |
| Bulletproof | Brain Octane | 32 | 946 | 63 | 32.95 | 0.52 | N/A* | Sourced from Coconut Oil |
| Bulletproof | Brain Octane Soft Gels | 2 | 58 | 4 | 19.99 | 5 | N/A* | Sourced from Coconut Oil |
| KetoSports | Keto8 | 12 | 355 | 24 | 19.97 | 0.83 | N/A* | Sourced from Palm Kernel Oil |
| MiCkey T | MiCkey T Eight | 32 | 946 | 63 | 32.95 | 0.52 | 0.9907 | Sourced from Palm and Coconut Oil |
| Parillo Performance | CapTri** | 32 | 946 | 63 | 30.63 | 0.63 | 0.99 | Sourced from Coconut Oil |
| KetoMCT Oil | KetoMCT** | 32 | 946 | 63 | 30.62 | 0.63 | 0.9779 | Sourced from Coconut and Palm Oil |
| Primal Fuel | Primal Fuel Reine Caprylsaure | 17 | 500 | 33 | 19.46 | 0.59 | 0.91 | Sourced from Coconut Oil |
| Ketosource | Pure C8 MCT Oil | 34 | 1000 | 67 | 29.66 | 0.44 | 0.998 | Sourced from Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO certified) and Coconut Oil, Certificate of Analysis made available |
| Ketosource | Pure C8 MCT Oil | 17 | 500 | 33 | 15.95 | 0.48 | 0.998 | Sourced from Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO certified) and Coconut Oil, Certificate of Analysis made available |
| Bulletproof | Brain Octane Go Packs | 8 | 225 | 15 | 16.95 | 1.13 | N/A* | Sourced from Coconut Oil |
| KetoLife | KetoLife C8 MCT Oil Sachets | 10 | 300 | 20 | 12.5 | 0.63 | 0.976 | Sourced from Coconut and Palm Oil |
| KetoLife | KetoLife C8 MCT Oil | 17 | 500 | 33 | 17.5 | 0.53 | 0.976 | Sourced from Coconut and Palm Oil |
** Prices estimated based on the US to UK conversion price.
Notes: Current UK prices updated monthly and are the suggested retail price (RRP) set by the product owners. Amazon prices are higher than the RRP due to Amazon commissions.
Concerns Over Use of Palm Oil in MCT Products
There are many concerns around the use of Palm Oil in MCT or C8 Products. We’ll write an article on this topic soon as it’s a common question and there is a lot of confusion and misinformation attached to it.
The quick takeaways however are:
- Functionally speaking, the source from which MCT products get their fatty acids is not an issue. Whether C8 MCTs or other MCTs come from coconut oil or palm oil doesnt matter. It’s the same fatty acids.
- There are environmental and sustainability concerns of products that rely on palm oil that is not sustainably farmed or produced. Palm oil production has led to the deforestation of many previously tropical areas. Thus, it accounts for more than 10% of CO2 emissions in the world. In addition, there are concerns over the burning and killing of Orangutans, which have been falling in number. They live in the trees in Indonesia, one of the world’s largest suppliers of palm oil. Check with product owners if palm oil used is sustainable by asking them about Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) certification.
Summary: The Main Takeaways
Caprylic acid (C8) shows potential for those following a keto diet.
Compared to generic MCT oil, pure caprylic acid oil products are a better bang for your buck. This is because capric acid (C10) and lauric acid (C12) increase ketones far less than caprylic acid. Therefore, lower ketone production suggests that capric and lauric acid don’t appear to be as readily metabolised for energy as caprylic acid.
However, more research is necessary to show whether or not the metabolic health benefits come from the caprylic acid or the other fatty acids.