Exogenous ketone supplements are growing in popularity. They are used as a means of boosting ketone levels in the blood. Here we take a look at how well popular exogenous ketone supplements can boost ketone levels.
This summary of the experiment covers the following:
- What Exogenous Ketone Supplements Are
- What the Experiment Was and Why We Did It
- How the Experiment Was Run
- The Experiment Results
- Cost Analysis
- Post Analysis – Strengths and Limitations
- Summary: The Takeaways
What Exogenous Ketone Supplements Are
Exogenous ketone supplements are supplements that boost levels of ketones in the blood.
Exogenous ketone supplements include ketone esters, ketone salts, MCT oils, and 1,3-butanediol.
You can also find supplements and foods that contain the above as “active ingredients”. For instance, there are MCT powders (containing C8 MCT oil or mixed MCT oil). There are also snacks and bars available (like the Ketone Bar) which contain these.
However, the ability of each powder and snack to boost ketone levels relies on the ketone ester, ketone salt, or MCT it contains. So we designed our experiment to test each of these ‘active ingredients’ in its isolated/ pure form.
What the Experiment Was and Why We Did It
We wanted to know how well each exogenous ketone supplement could boost levels of beta-hydroxybutyrate. This is also known as BHB ketone. It is the ketone body that is measured by handheld blood meters and often used in studies.
To do this, we tested blood ketone and glucose responses to the most popular exogenous ketone supplements at the time to know for sure.
How the Experiment Was Run
What Was Tested?
For the experiment, two participants took four days’ worth of baseline readings. These measured blood levels of glucose and BHB ketone.
Next, participants tested one exogenous ketone supplement per week. Seven days was left between each test as a ‘washout period’. This made sure that there were no leftover effects from one test spilling over to another.
Here are the ketone supplements that were tested:
- HVMN Ketone Ester (now discontinued – it was licensed from TΔS)
- KE4 ketone Aid Ketone Ester
- KetoCaNa Ketone Salt
- Pruvit Keto OS Max Ketone Salt (now discontinued)
- Ketosource Pure C8 MCT Oil
Table 1: The five ketone supplements used in the experiment and their dosages
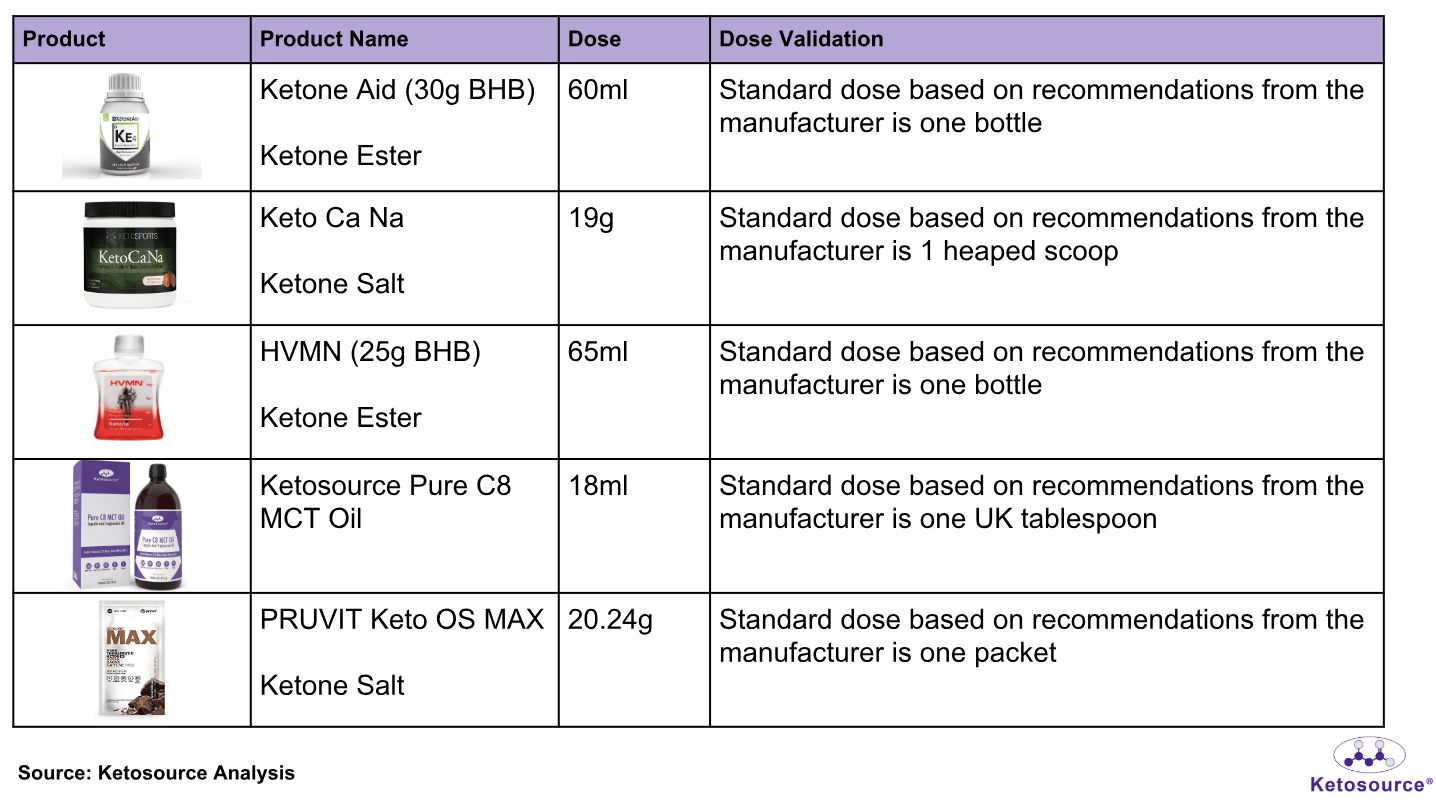
*The HVMN and Pruvit products listed here are now discontinued
**One UK tablespoon is now known to be 15ml. This has been corrected on the nutrition label for Pure C8 MCT Oil. A dose of 18ml was used in this experiment.
How Did We Prepare For The Experiment? Who Did It?
Here are some details for the participants:
- Two participants (one male and one female) both tested all exogenous ketone supplements one time each.
- Both participants had been following a ketogenic diet for at least two years. They each had measurable levels of blood BHB ketones at the time of testing.
In order for the experiments to go ahead, each participant:
- Had their final meal no later than 7.30pm the previous evening
- Had a good amount of sleep the previous night
- Took no food, drink or exercise upon waking
These ‘lifestyle factors’ are known to influence ketone levels. So this approach helped ensure that nothing interfered with the participants’ responses.
How Did We Do The Experiment?
Figure 1. Overview of the testing procedure
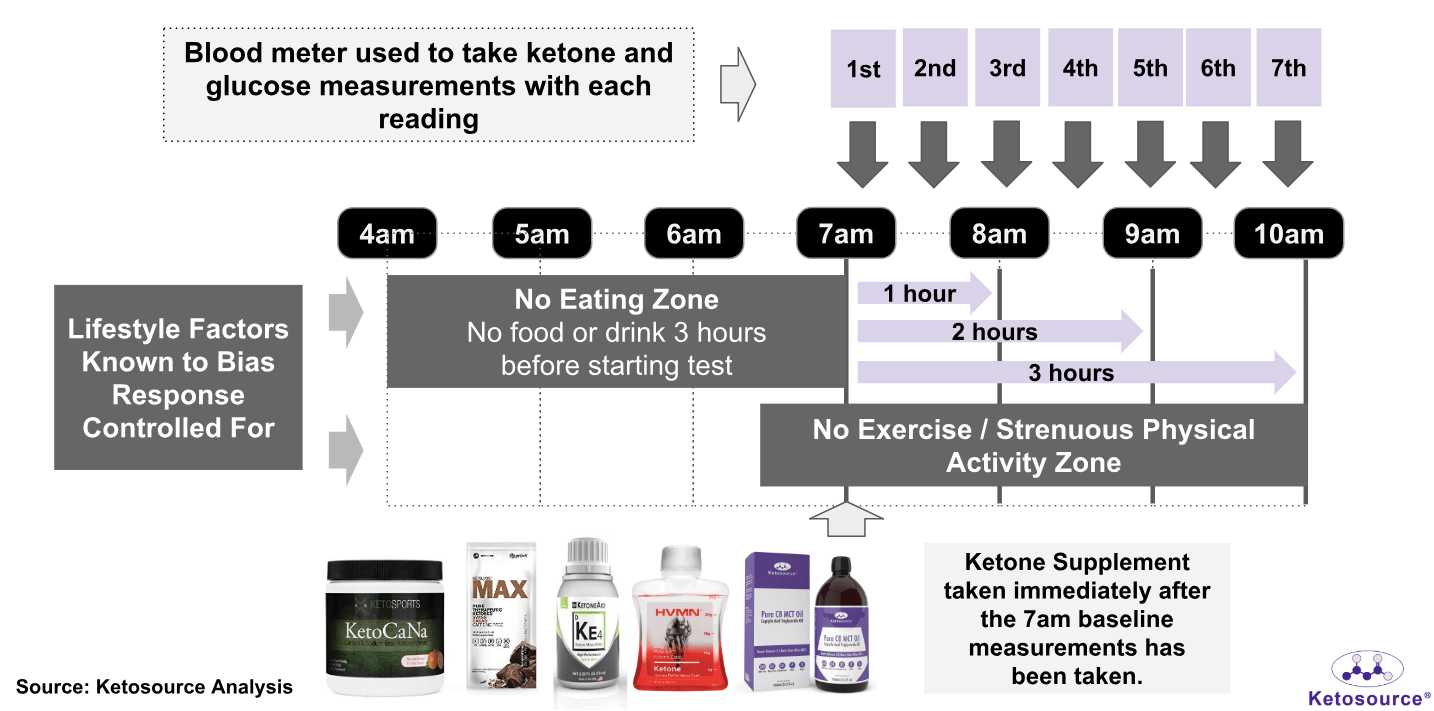
A pre-testing survey was completed by each participant before each test. This survey addressed variables that may confound the responses to the supplements. These included:
- Sleep Quality and Duration
- Energy Levels Compared to Normal
- Illness
- Weight Measurement
- Waist Measurements
- Current Medication
- Time Finished Last Meal
- Last Time to Exercise
After the survey, resting blood BHB ketone and blood glucose measurements were taken. The participants used the OnCall Dual Glucose Ketone Monitor for these measurements (we now use the Keto-Mojo meter) These baseline measurements were followed by the consumption of one exogenous ketone supplement.
Levels of blood BHB ketone and blood glucose were measured every 30 minutes. Measurements were taken for a total of three hours. Participants resumed their normal day-to-day activities after each test.
The Experiment Results
Average Blood BHB Ketone Responses
Figure 2. Average blood BHB ketone levels following consumption of each exogenous ketone supplement
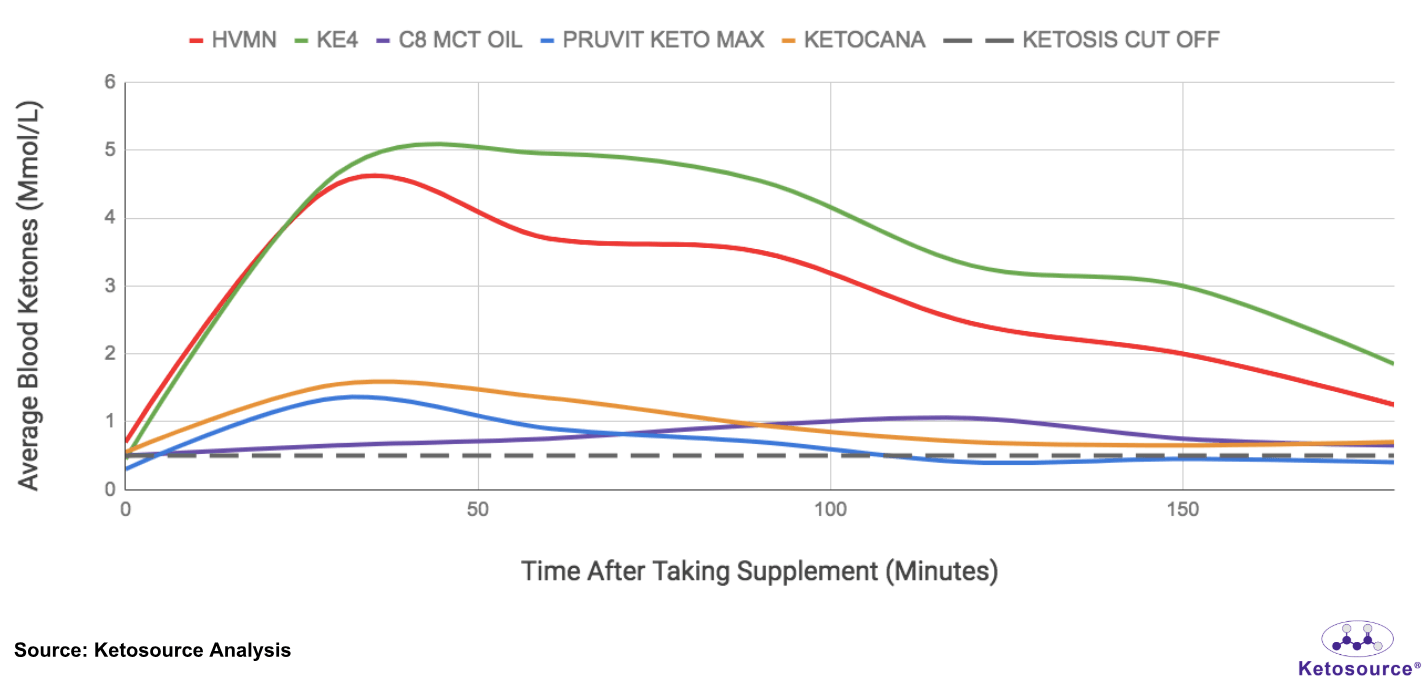
As expected, we saw the ketone esters boost BHB ketone levels much higher than the ketone salts or C8 MCT oil.
On average, both the esters and salts had their maximal effects after 30-60 minutes. This is similar to results from published studies.
In contrast, it took 120 minutes on average for C8 MCT oil to do the same. This is longer than the expected results for C8 MCT oil.
One possible explanation for this is that both participants were on ketogenic diets during the experiment. On average, the participants were at or near appetite reduction ketosis at the start of each test. This is the BHB level where you can expect a reduced appetite. It is often referred to simply as ‘ketosis’ or ‘nutritional ketosis’. The participants’ baseline ketogenic metabolism may have effected their responses to C8 MCT oil.
The BHB ketone boost lasted longer for the esters compared to the salts or C8 MCT oil. BHB ketone levels returned to baseline after 120 minutes following salt consumption. But they remained boosted 180 minutes following consumption of the ester.
Average Blood Glucose Responses
Figure 3. Average blood glucose levels following consumption of each exogenous ketone supplement
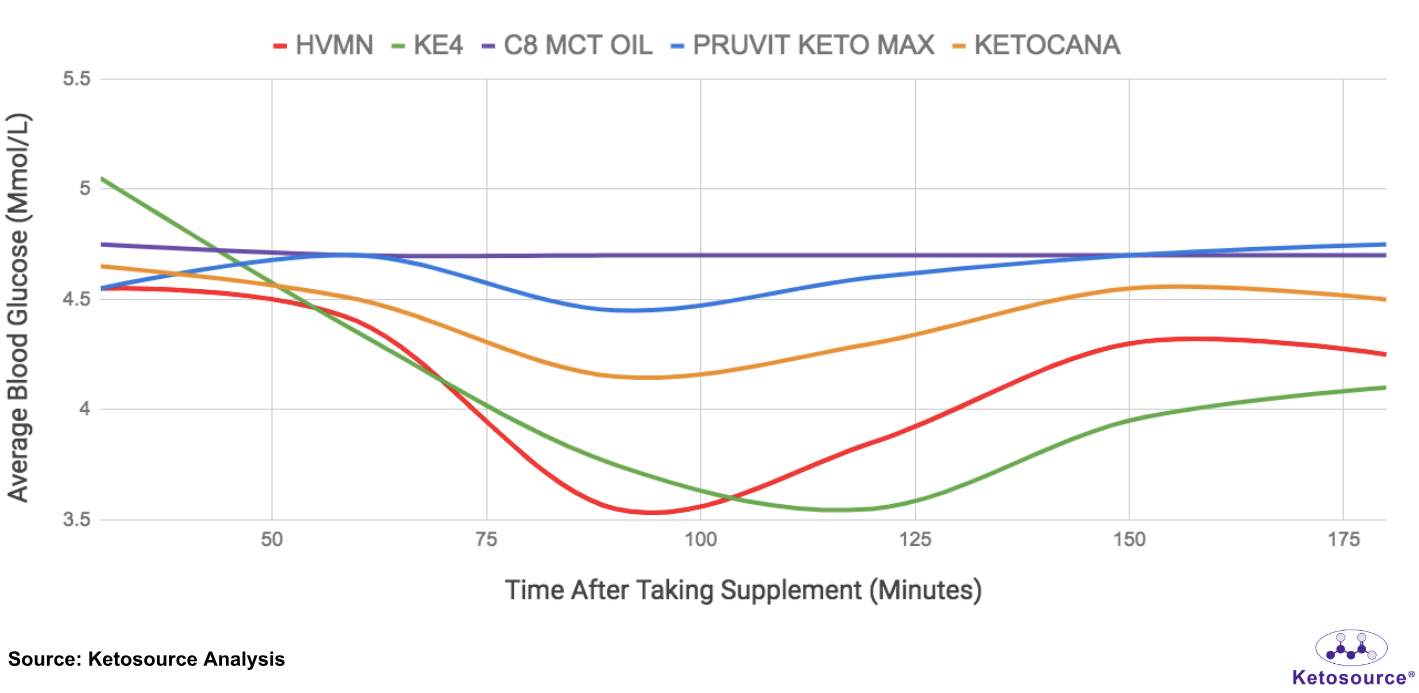
We saw that the ketone esters and ketone salts reduced blood glucose levels, whereas the C8 MCT oil did not. Similar to the BHB ketone boosts, this effect was most pronounced with the ketone esters. Blood glucose levels remained lower at 180 minutes following consumption of either ketone ester.
Cost Analysis
Figure 4. The cost per serving and peak BHB ketone boosts for each exogenous ketone supplement
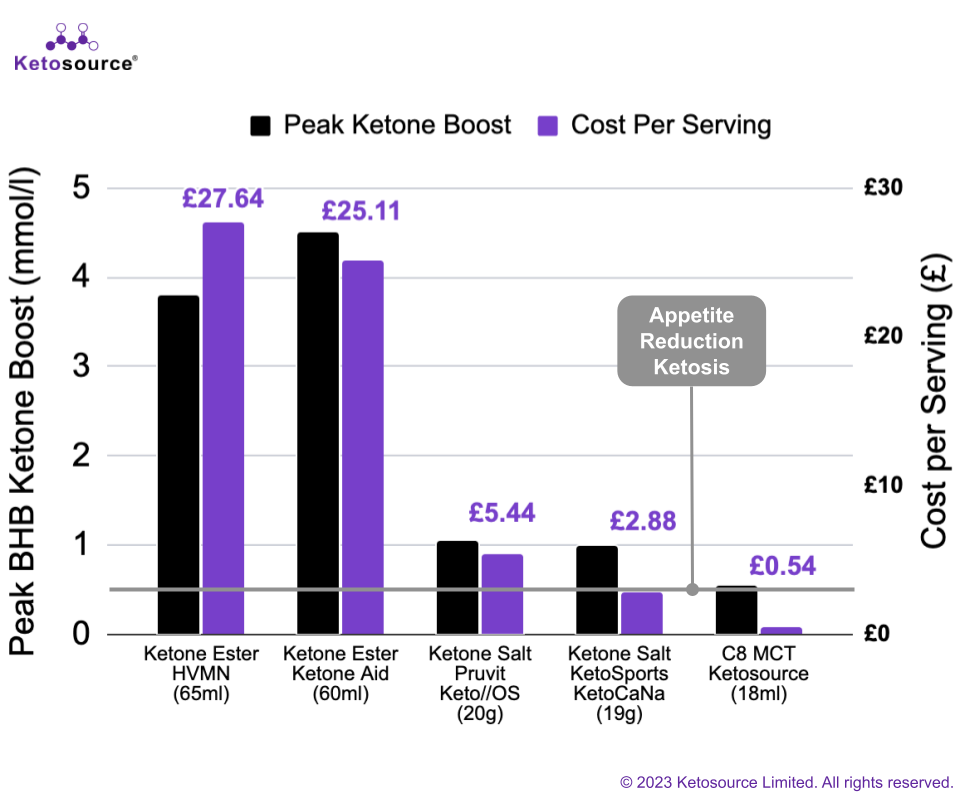
In general, the cost per serving for each exogenous ketone supplement tracked with its peak BHB ketone boost. Ketone esters give the highest BHB ketone boost and cost the most per serving. Salts cost much less per serving than esters but also give a smaller BHB ketone boost. C8 MCT oil costs the least per serving and boosts BHB ketones by the smallest amount.
Post Analysis – Strengths and Limitations
A wide selection of exogenous ketone supplements were tested at the recommended serving sizes.
Some of these supplements are now discontinued. So follow-up studies will be needed to continue testing popular options on the market.
Blood glucose and BHB ketone responses were recorded every 30 minutes for each test. This is consistent with similar studies.
The test duration of 180 minutes did not capture the full response to some of the exogenous ketone supplements. So follow-up studies may track responses for longer periods of time.
For example, continuous glucose monitors and continuous ketone monitors could be used. These would allow for tracking over several weeks. They could provide greater insights into the long-term effects of each supplement.
The study was most limited by the number of participants. More participants would allow for deeper analysis. Various analyses could be performed based on differences in biology and lifestyle. These could include differences in diet, body size, exercise regimen, and biological sex.
Diet may be especially important here. Both participants in this experiment were on ketogenic diets. Follow-up studies using other baseline diets could help with setting expectations for those diets.
Final Thoughts
We found that ketone esters provided the largest BHB ketone boost per serving. This is followed by ketone salts and finally C8 MCT oil. These results are similar to those in published studies.
Our cost analysis showed that, in general, you pay more for a larger BHB ketone boost. So the most cost-effective option for you depends on your target ketone level.
If your goal is fat loss, then any of the exogenous ketone supplements we tested will work. They can all help you reach appetite reduction ketosis. Check out this step-by-step guide if you’d like to use C8 MCT oil for this.
Watch the Ketone Ester Tasting Videos
Video 1: Taste Test Watch here to see the participants taste the HVMN ketone ester for the first time
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jwAJSidDLK4&list=UUziOg3-ynLOP7c6rLpdnUxA&index=2
Video 2: Taste Test Watch here to see the participants taste the KetoneAid ketone ester for the first time
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OuwWBzXEVF0&list=UUziOg3-ynLOP7c6rLpdnUxA&index=1
Summary: The Takeaways
- We confirmed that exogenous ketone supplements boost BHB ketone levels to varying degrees.
- All of the exogenous ketone supplements tested boosted BHB ketone levels. Ketone esters caused the largest boost, then ketone salts, and then C8 MCT oil.
- Ketone esters and ketone salts boosted BHB ketone levels to their peaks within 30 minutes. C8 MCT oil took longer with a peak at two hours.
- In general, you can expect to pay more for a higher BHB ketone boost. So the most cost-effective option for you depends on your target ketone level.
- All of the exogenous ketone supplements we tested can help you reach appetite reduction ketosis. So you can choose any of them if your goal is fat loss.
QUESTIONS: Have you been taking Ketone Supplements or have you tried Ketone Esters? What would you like us to test next? Let us know by adding to them
in the comments.
Research References
{5748374:B6PYTZL3};{5748374:P9KSH38T},{5748374:VKS54E7J};{5748374:P9KSH38T};{5748374:VKS54E7J};{5748374:B6PYTZL3},{5748374:WUYUM7TU};{5748374:P9KSH38T},{5748374:VKS54E7J};{5748374:P9KSH38T},{5748374:VKS54E7J}
3d-printed-materials-and-systems
asc
0
7338
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3A%22zotpress-31db46e58d5cd3562997908975b19086%22%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A0%2C%22request_next%22%3A0%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%22WUYUM7TU%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Norgren%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222019-12-10%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22clear%3A%20left%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-left-margin%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22float%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%5C%22%3E1.%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-right-inline%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22margin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%5C%22%3ENorgren%20J%2C%20Sindi%20S%2C%20Sandebring-Matton%20A%2C%20et%20al%20%282019%29%20Capillary%20blood%20tests%20may%20overestimate%20ketosis%3A%20triangulation%20between%20three%20different%20measures%20of%20%26%23x3B2%3B-hydroxybutyrate.%20American%20Journal%20of%20Physiology-Endocrinology%20and%20Metabolism%20318%3AE184%26%23x2013%3BE188.%20%3Ca%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00454.2019%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00454.2019%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%20%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Capillary%20blood%20tests%20may%20overestimate%20ketosis%3A%20triangulation%20between%20three%20different%20measures%20of%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jakob%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Norgren%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shireen%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sindi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sandebring-Matton%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ingemar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22K%5Cu00e5reholt%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ulrika%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Akenine%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Karin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nordin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Staffan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rosenborg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tiia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ngandu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Miia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kivipelto%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22The%20ketone%20body%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%20%28BHB%29%2C%20assessed%20by%20a%20point-of-care%20meter%20in%20venous%20whole%20blood%20%28BHBv%29%2C%20was%20used%20as%20the%20main%20outcome%20in%20a%20study%20on%20nutritional%20ketosis%20in%20healthy%20older%20adults.%20Two%20other%20BHB%20measures%20were%20also%20used%20in%20the%20study%20for%20validation%20and%20exploratory%20purposes%2C%20and%20here%20we%20report%20findings%20on%20correlation%20and%20agreement%20between%20those%20three%20methods.%20Ketosis%20in%20the%20range%20of%200%5Cu20131.5%20mmol%5C%2FL%20was%20induced%20in%2015%20healthy%20volunteers%20by%20intake%20of%20medium-chain%20fatty%20acids%20after%20a%2012-h%20fast.%20BHBv%20was%20assessed%20at%2012%20time%20points%20for%204%20h.%20The%20same%20point-of-care%20meter%20was%20also%20used%20to%20test%20capillary%20blood%20%28BHBc%29%20at%20three%20time%20points%2C%20and%20a%20laboratory%20test%20determined%20total%20ketones%20%28TK%29%20in%20plasma%20%28BHBp%20%2B%20acetoacetate%29%20at%20four%20time%20points.%20A%20total%20of%20180%20cases%20included%20simultaneous%20data%20on%20BHBv%2C%20BHBc%2C%20BHBp%2C%20and%20TK.%20TK%20correlated%20with%20BHBp%20%28Pearson%5Cu2019s%20r%5Cu2009%3D%5Cu20090.99%29%2C%20BHBv%20%28r%5Cu2009%3D%5Cu20090.91%29%2C%20and%20BHBc%20%28r%5Cu2009%3D%5Cu20090.91%29%2C%20all%20P%20%3C%200.0001.%20BHBv%20and%20BHBp%20had%20good%20agreement%20in%20absolute%20values.%20However%2C%20the%20slope%20between%20BHBc%20and%20BHBv%2C%20measured%20with%20the%20same%20device%2C%20was%20in%20the%20range%20of%200.64%5Cu20130.78%20in%20different%20regression%20models%2C%20indicating%20substantially%20higher%20BHB%20concentrations%20in%20capillary%20versus%20venous%20blood.%20We%20conclude%20that%20all%20three%20methods%20are%20valid%20to%20detect%20relative%20changes%20in%20ketosis%2C%20but%20our%20results%20highlight%20the%20importance%20of%20method%20considerations%20and%20the%20possible%20need%20to%20adjust%20cutoffs%2C%20e.g.%2C%20in%20the%20management%20of%20ketoacidosis%20and%20in%20the%20evaluation%20and%20comparison%20of%20dietary%20interventions.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22December%2010%2C%202019%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00454.2019%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220193-1849%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.physiology.org%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2Ffull%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00454.2019%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22JYIQJBU4%22%2C%22XNQZ77UF%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-02-01T14%3A40%3A00Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22B6PYTZL3%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Gibson%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22clear%3A%20left%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-left-margin%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22float%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%5C%22%3E1.%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-right-inline%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22margin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%5C%22%3EGibson%20AA%2C%20Seimon%20RV%2C%20Lee%20CMY%2C%20et%20al%20%282015%29%20Do%20ketogenic%20diets%20really%20suppress%20appetite%3F%20A%20systematic%20review%20and%20meta-analysis.%20Obes%20Rev%2016%3A64%26%23x2013%3B76.%20%3Ca%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fobr.12230%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fobr.12230%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%20%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Do%20ketogenic%20diets%20really%20suppress%20appetite%3F%20A%20systematic%20review%20and%20meta-analysis%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gibson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Seimon%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20M.%20Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lee%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ayre%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Franklin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Markovic%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22I.%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Caterson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sainsbury%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Very-low-energy%20diets%20%28VLEDs%29%20and%20ketogenic%20low-carbohydrate%20diets%20%28KLCDs%29%20are%20two%20dietary%20strategies%20that%20have%20been%20associated%20with%20a%20suppression%20of%20appetite.%20However%2C%20the%20results%20of%20clinical%20trials%20investigating%20the%20effect%20of%20ketogenic%20diets%20on%20appetite%20are%20inconsistent.%20To%20evaluate%20quantitatively%20the%20effect%20of%20ketogenic%20diets%20on%20subjective%20appetite%20ratings%2C%20we%20conducted%20a%20systematic%20literature%20search%20and%20meta-analysis%20of%20studies%20that%20assessed%20appetite%20with%20visual%20analogue%20scales%20before%20%28in%20energy%20balance%29%20and%20during%20%28while%20in%20ketosis%29%20adherence%20to%20VLED%20or%20KLCD.%20Individuals%20were%20less%20hungry%20and%20exhibited%20greater%20fullness%5C%2Fsatiety%20while%20adhering%20to%20VLED%2C%20and%20individuals%20adhering%20to%20KLCD%20were%20less%20hungry%20and%20had%20a%20reduced%20desire%20to%20eat.%20Although%20these%20absolute%20changes%20in%20appetite%20were%20small%2C%20they%20occurred%20within%20the%20context%20of%20energy%20restriction%2C%20which%20is%20known%20to%20increase%20appetite%20in%20obese%20people.%20Thus%2C%20the%20clinical%20benefit%20of%20a%20ketogenic%20diet%20is%20in%20preventing%20an%20increase%20in%20appetite%2C%20despite%20weight%20loss%2C%20although%20individuals%20may%20indeed%20feel%20slightly%20less%20hungry%20%28or%20more%20full%20or%20satisfied%29.%20Ketosis%20appears%20to%20provide%20a%20plausible%20explanation%20for%20this%20suppression%20of%20appetite.%20Future%20studies%20should%20investigate%20the%20minimum%20level%20of%20ketosis%20required%20to%20achieve%20appetite%20suppression%20during%20ketogenic%20weight%20loss%20diets%2C%20as%20this%20could%20enable%20inclusion%20of%20a%20greater%20variety%20of%20healthy%20carbohydrate-containing%20foods%20into%20the%20diet.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22Jan%202015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22eng%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1111%5C%2Fobr.12230%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221467-789X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22IB4QNEHC%22%2C%224BU4YKKK%22%2C%22RC4FYWNC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222019-10-04T14%3A28%3A40Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22VKS54E7J%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22St-Pierre%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222019-04-16%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22clear%3A%20left%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-left-margin%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22float%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%5C%22%3E1.%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-right-inline%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22margin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%5C%22%3ESt-Pierre%20V%2C%20Vandenberghe%20C%2C%20Lowry%20C-M%2C%20et%20al%20%282019%29%20Plasma%20Ketone%20and%20Medium%20Chain%20Fatty%20Acid%20Response%20in%20Humans%20Consuming%20Different%20Medium%20Chain%20Triglycerides%20During%20a%20Metabolic%20Study%20Day.%20Front%20Nutr%206%3A.%20%3Ca%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffnut.2019.00046%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffnut.2019.00046%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%20%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Plasma%20Ketone%20and%20Medium%20Chain%20Fatty%20Acid%20Response%20in%20Humans%20Consuming%20Different%20Medium%20Chain%20Triglycerides%20During%20a%20Metabolic%20Study%20Day%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Val%5Cu00e9rie%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22St-Pierre%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Camille%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vandenberghe%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Carolyne-Mary%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lowry%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M%5Cu00e9lanie%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fortier%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Christian-Alexandre%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Castellano%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wagner%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Stephen%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cunnane%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Background%3A%20Medium%20chain%20triglycerides%20%28MCT%29%20are%20ketogenic%20but%20the%20relationship%20between%20the%20change%20in%20plasma%20ketones%20and%20the%20change%20plasma%20medium%20chain%20fatty%20acids%20%28MCFA%29%5Cu2014octanoate%2C%20decanoate%2C%20or%20dodecanoate%5Cu2014after%20an%20oral%20dose%20of%20MCT%20is%20not%20well-known.%20An%208%20h%20metabolic%20study%20day%20is%20a%20suitable%20model%20to%20assess%20the%20acute%20effects%20on%20plasma%20ketones%20and%20MCFA%20after%20a%20dose%20of%20tricaprylin%20%28C8%29%2C%20tricaprin%20%28C10%29%2C%20trilaurin%20%28C12%29%20or%20mixed%20MCT%20%28C8C10%29.%2C%20Objective%3A%20To%20assess%20in%20healthy%20humans%20the%20relationship%20between%20the%20change%20in%20plasma%20ketones%2C%20and%20octanoate%2C%20decanoate%20and%20dodecanoate%20in%20plasma%20total%20lipids%20during%20an%208%20h%20metabolic%20study%20day%20in%20which%20a%20first%2020%20ml%20dose%20of%20the%20homogenized%20test%20oil%20is%20taken%20with%20breakfast%20and%20a%20second%2020%20ml%20dose%20is%20taken%204%20h%20later%20without%20an%20accompanying%20meal.%2C%20Results%3A%20The%20change%20in%20plasma%20acetoacetate%2C%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%20and%20total%20ketones%20was%20highest%20after%20C8%20%280.5%20to%203%20h%20post-dose%29%20and%20was%20lower%20during%20tests%20in%20which%20octanoate%20was%20absent%20or%20was%20diluted%20by%20C10%20in%20the%20test%20oil.%20The%20plasma%20ketone%20response%20was%20also%20about%202%20fold%20higher%20without%20an%20accompanying%20meal%20%28P%20%3D%200.012%29.%20However%2C%20except%20during%20the%20pure%20C10%20test%2C%20the%20response%20of%20octanoate%2C%20decanoate%20or%20dodecanoate%20in%20plasma%20total%20lipids%20to%20the%20test%20oils%20was%20not%20affected%20by%20consuming%20an%20accompanying%20meal.%20Except%20with%20C12%2C%20the%204%20h%20area-under-the-curve%20of%20plasma%20%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%5C%2Facetoacetate%20was%202%5Cu20133%20fold%20higher%20when%20no%20meal%20was%20consumed%20%28P%20%3C%200.04%29.%2C%20Conclusion%3A%20C8%20was%20about%20three%20times%20more%20ketogenic%20than%20C10%20and%20about%20six%20times%20more%20ketogenic%20than%20C12%20under%20these%20acute%20metabolic%20test%20conditions%2C%20an%20effect%20related%20to%20the%20post-dose%20increase%20in%20octanoate%20in%20plasma%20total%20lipids.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222019-4-16%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3389%5C%2Ffnut.2019.00046%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222296-861X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpmc%5C%2Farticles%5C%2FPMC6481320%5C%2F%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22HJKVZCPI%22%2C%22XNQZ77UF%22%2C%223WAB5Z2C%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222019-06-28T15%3A53%3A24Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22P9KSH38T%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5748374%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Stubbs%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222017%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%201.35%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22clear%3A%20left%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-left-margin%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22float%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%5C%22%3E1.%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-right-inline%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22margin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%5C%22%3EStubbs%20BJ%2C%20Cox%20PJ%2C%20Evans%20RD%2C%20et%20al%20%282017%29%20On%20the%20Metabolism%20of%20Exogenous%20Ketones%20in%20Humans.%20Front%20Physiol%208%3A.%20%3Ca%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphys.2017.00848%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphys.2017.00848%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%20%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22On%20the%20Metabolism%20of%20Exogenous%20Ketones%20in%20Humans%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Brianna%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Stubbs%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Pete%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cox%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rhys%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Evans%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Peter%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Santer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jack%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Miller%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Olivia%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Faull%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Snapper%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Magor-Elliott%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Satoshi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hiyama%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Matthew%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Stirling%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kieran%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Clarke%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Background%20and%20aims%3A%20Currently%20there%20is%20considerable%20interest%20in%20ketone%20metabolism%20owing%20to%20recently%20reported%20benefits%20of%20ketosis%20for%20human%20health.%20Traditionally%2C%20ketosis%20has%20been%20achieved%20by%20following%20a%20high-fat%2C%20low-carbohydrate%20%5Cu2018ketogenic%5Cu2019%20diet%2C%20but%20adherence%20to%20such%20diets%20can%20be%20difficult.%20An%20alternative%20way%20to%20increase%20blood%20D-%5Cu03b2-hydroxybutyrate%20%28D-%5Cu03b2HB%29%20concentrations%20is%20ketone%20drinks%2C%20but%20the%20metabolic%20effects%20of%20exogenous%20ketones%20are%20relatively%20unknown.%20Here%2C%20healthy%20human%20volunteers%20took%20part%20in%20three%20randomized%20metabolic%20studies%20of%20drinks%20containing%20a%20ketone%20ester%20%28KE%29%3B%20%28R%29-3-hydroxybutyl-%28R%29-1%2C3-hydroxybutyrate%2C%20or%20ketone%20salts%20%28KS%29%3B%20sodium%20plus%20potassium%20%5Cu03b2HB.%20Methods%20and%20Results%3A%20In%20the%20first%20study%2C%2015%20participants%20consumed%20KE%20or%20KS%20drinks%20that%20delivered%20~12%20g%20or%20~24%20g%20of%20%5Cu03b2HB.%20Both%20drinks%20elevated%20blood%20D-%5Cu03b2HB%20concentrations%20%28D-%5Cu03b2HB%20Cmax%3A%20KE%202.8%20mM%2C%20KS%201.0%20mM%2C%20P%20%3C%200.001%29%2C%20which%20returned%20to%20baseline%20within%203-4%20h.%20KS%20drinks%20were%20found%20to%20contain%2050%25%20of%20the%20L-%5Cu03b2HB%20isoform%2C%20which%20remained%20elevated%20in%20blood%20for%20over%208%20h%2C%20but%20was%20not%20detectable%20after%2024%20h.%20Urinary%20excretion%20of%20both%20D-%5Cu03b2HB%20and%20L-%5Cu03b2HB%20was%20%3C%201.5%20%25%20of%20the%20total%20%5Cu03b2HB%20ingested%20and%20was%20in%20proportion%20to%20the%20blood%20AUC.%20D-%5Cu03b2HB%2C%20but%20not%20L-%5Cu03b2HB%2C%20was%20slowly%20converted%20to%20breath%20acetone.%20The%20KE%20drink%20decreased%20blood%20pH%20by%200.10%20and%20the%20KS%20drink%20increased%20urinary%20pH%20from%205.7%20to%208.5.%20In%20the%20second%20study%2C%20the%20effect%20of%20a%20meal%20before%20a%20KE%20drink%20on%20blood%20D-%5Cu03b2HB%20concentrations%20was%20determined%20in%2016%20participants.%20Food%20lowered%20blood%20D-%5Cu03b2HB%20Cmax%20by%2033%25%20%28Fed%202.2%20mM%2C%20Fasted%203.3%20mM%2C%20P%20%3C%200.001%29%2C%20but%20did%20not%20alter%20acetoacetate%20or%20breath%20acetone%20concentrations.%20All%20ketone%20drinks%20lowered%20blood%20glucose%2C%20free%20fatty%20acid%20and%20triglyceride%20concentrations%2C%20and%20had%20similar%20effects%20on%20blood%20electrolytes%2C%20which%20remained%20normal.%20In%20the%20final%20study%2C%20participants%20were%20given%20KE%20over%209%20h%20as%20three%20drinks%20%28n%20%3D%2012%29%20or%20a%20continuous%20nasogastric%20infusion%20%28n%20%3D%204%29%20to%20maintain%20blood%20D-%5Cu03b2HB%20concentrations%20greater%20than%201%20mM.%20Both%20drinks%20and%20infusions%20gave%20identical%20D-%5Cu03b2HB%20AUC%20of%201.3-1.4%20moles.min.%20Conclusion%3A%20We%20conclude%20that%20exogenous%20ketone%20drinks%20are%20a%20practical%2C%20efficacious%20way%20to%20achieve%20ketosis.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222017%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22English%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3389%5C%2Ffphys.2017.00848%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221664-042X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.frontiersin.org%5C%2Farticles%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphys.2017.00848%5C%2Ffull%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22TPPQF3UK%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222019-06-18T06%3A02%3A18Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D
1.
Norgren J, Sindi S, Sandebring-Matton A, et al (2019) Capillary blood tests may overestimate ketosis: triangulation between three different measures of β-hydroxybutyrate. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 318:E184–E188.
https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00454.2019
1.
Gibson AA, Seimon RV, Lee CMY, et al (2015) Do ketogenic diets really suppress appetite? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 16:64–76.
https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12230
1.
St-Pierre V, Vandenberghe C, Lowry C-M, et al (2019) Plasma Ketone and Medium Chain Fatty Acid Response in Humans Consuming Different Medium Chain Triglycerides During a Metabolic Study Day. Front Nutr 6:.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00046




